| Lesson 7 | Organizational units |
| Objective | Define an organizational unit. |
Delegating Control of Organization Units in Active Directory: A Step-by-Step Guide
Delegating control of Organization Units (OUs) in Active Directory (AD) is a critical administrative task that allows you to grant specific permissions to users or groups, enabling them to manage resources within the OU without having full domain administrative privileges. This practice not only enhances security by following the principle of least privilege but also improves efficiency by distributing administrative tasks among various individuals or teams. Here is a step-by-step guide to delegate control of OUs in Active Directory:
By following these steps, you can successfully delegate control of Organization Units in Active Directory, granting specific permissions to selected users or groups. This process allows for better security and efficiency within your organization by ensuring that users have only the necessary privileges to perform their assigned tasks.
- Launch the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) snap-in:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type "dsa.msc" (without quotes) and press Enter to open the ADUC snap-in.
- Locate the Organization Unit:
- In the ADUC console, navigate to the OU you want to delegate control over. You can find it under your domain tree structure.
- Initiate the Delegation of Control Wizard:
- Right-click the OU and select "Delegate Control" from the context menu to start the Delegation of Control Wizard.
- Select the Users or Groups:
- In the Delegation of Control Wizard, click "Next" to proceed.
- Click "Add" to select the users or groups to whom you want to delegate control. You can either type the name of the user/group or click "Advanced" to search for specific users/groups.
- Once the desired users/groups are selected, click "OK" and then "Next" to continue.
- Specify the Permissions:
- In the "Tasks to Delegate" window, you can either choose from a list of common tasks (e.g., "Create, delete, and manage user accounts") or click "Customize" for more granular control over permissions.
- If you select "Customize," click "Next" and then click "Add" in the "Permissions" window to choose specific permissions from the list. Be sure to select the appropriate object types (e.g., User, Group, Computer) to apply the permissions to.
- Once you have specified the desired permissions, click "OK" and then "Next" to continue.
- Review and Complete the Delegation Process:
- Verify the summary of the delegated permissions to ensure accuracy.
- Click "Finish" to complete the delegation process.
By following these steps, you can successfully delegate control of Organization Units in Active Directory, granting specific permissions to selected users or groups. This process allows for better security and efficiency within your organization by ensuring that users have only the necessary privileges to perform their assigned tasks.
Organizational Units are areas of Organization within the Active Directory
An organizational unit (OU) is a container object that you use to organize objects within a domain. An OU contains objects, such as user accounts, groups, computers, printers, and other OUs.
Organizational unit','An organizational unit (OU) is a container object that you use to organize objects within a domain. An OU contains objects, such as user accounts, groups, computers, printers, and other OUs.
Organizational unit','An organizational unit (OU) is a container object that you use to organize objects within a domain. An OU contains objects, such as user accounts, groups, computers, printers, and other OUs.
You can use OUs to group objects into a logical hierarchy to represent:
As you can see above, the OU hierarchy within a domain is independent of the OU hierarchy structure of other domains. In other words, each domain can implement its own OU hierarchy.
- An organizational structure based on departmental or geographical boundaries or
- A network administrative model based on administrative responsibilities
As you can see above, the OU hierarchy within a domain is independent of the OU hierarchy structure of other domains. In other words, each domain can implement its own OU hierarchy.
Delegating control of OUs
If you need to, you can delegate administrative control over the objects within an OU. This is easier if your system follows a
single domain model .
To delegate administrative control of an OU, you grant specific permissions for the OU and the objects that it contains to one or more users and groups. For an OU, there are two kinds of permissions that you can assign-complete control and limited control. The images below will show you why you might choose one form over the other.
To delegate administrative control of an OU, you grant specific permissions for the OU and the objects that it contains to one or more users and groups. For an OU, there are two kinds of permissions that you can assign-complete control and limited control. The images below will show you why you might choose one form over the other.
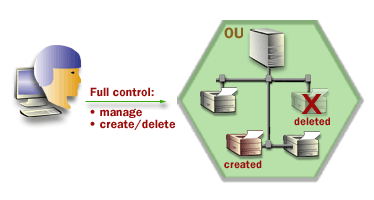
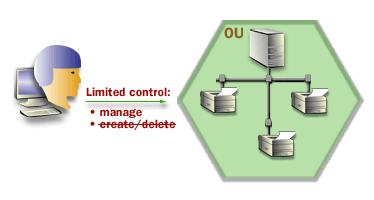
As you will come to realize, these permissions options are very useful.
In the next lesson, you will learn about trees and forests in detail.
In the next lesson, you will learn about trees and forests in detail.
