| Lesson 8 | Verify Active Directory installation |
| Objective | How to Verify your Installation of Active Directory. |
How to verify your Installation of Active Directory
After you install Active Directory, it is important to verify that the necessary directory database files, system volumes (security policies and files),
and DNS SRV resource records are created so that Active Directory works properly.
Verifying SRV resource records
After the installation of Active Directory, each DNS database file will contain SRV resource records, which are pointers to DNS hosts running Active Directory services. You should verify that the SRV resource records have been created for the domain controller after promotion. There are two ways to do this:
- If you are using a server running the DNS Server service, you can use DNS in Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
- If you are using a DNS service that does not support dynamic updates, you will need to manually register the SRV resource records.
Now view the Netlogon.dns file that is located in systemroot\System32\Config on each Active Directory domain controller.
The SRV resource records are listed in the standard DNS resource record text representation.
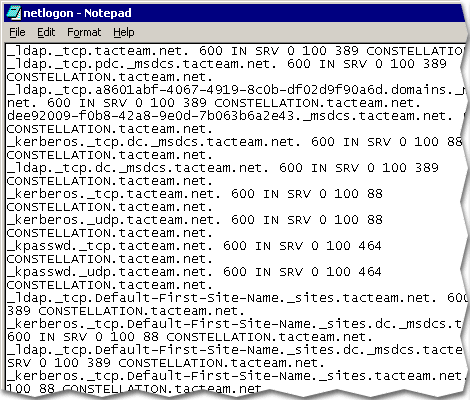
You will see the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) SRV record in the form:
_ldap._tcp. Active_Directory_domain_name IN SRV 0 100 389 domain_controller_name
If you install the DNS Server service during Active Directory installation, you must manually create a reverse lookup zone and set the zone attribute to Allow dynamic updates after installation.
_ldap._tcp. Active_Directory_domain_name IN SRV 0 100 389 domain_controller_name
If you install the DNS Server service during Active Directory installation, you must manually create a reverse lookup zone and set the zone attribute to Allow dynamic updates after installation.
Verify SRV resource record registration
Is the "SRV resource record registration" still used in Active Directory on Windows Server 2022?
After Active Directory is installed, you can also use the Nslookup command-line utility to verify that the domain controller registered its SRV resource records in the DNS database. To verify that SRV resource records[1] were properly registered by using Nslookup, perform the following steps:
- Open a command prompt.
- At the command prompt, type nslookup and then press Enter.
- Type ls -t SRV domain.msft (where domain.msft is your domain name), and then press Enter.
- If the SRV resource records were properly created, they will be listed. To save the results of this list to a file, type ls -t SRV domain.msft > File.
Nslookup generates a reverse lookup to determine the host name of the DNS server based on its IP address.
| Items | Post-installation location |
| Database | The database file for the new domain is stored in Active Directory. The default location for the database and database log files is systemroot\Ntds. However, you may want to place these files on a separate hard disk to improve read-write access. |
| Shared system volume | The shared system volume is hosted on all Windows 2000 domain controllers. It stores scripts that are part of the group policy objects for both the current domain and the enterprise network. The default location for the shared system volume is systemroot\Sysvol. The shared system volume must be located on an NTFS partition. |
| Default first site name | The first site is automatically created when you install and promote the first domain controller. It is called Default-First-Site-Name and it contains the first domain controller. You can create additional sites later. |
| Global catalog server | The first domain controller in the forest becomes a global catalog server by default. Additional global catalog servers can be configured by using Active Directory Sites and Services. |
| Root domain | The forest root domain is created when the first domain controller is installed. |
| Default containers | When the first domain is created, the following are created automatically:
|
| Default Domain Controllers OU | Domain Controllers contain the first domain controller, and other domain controllers as they are added to the domain. |
Verifying Server Promotion
You can also verify the promotion of a server by ensuring that the items in the View table are installed correctly.
The next lesson wraps up this module.
The next lesson wraps up this module.
[1]SRV resource records: Used in a DNS zone to register and locate well known TCP/IP services
