| Lesson 3 | Email agents |
| Objective | Define the roles of the three email system agents. |
Roles of Three email System Agents
Moving email from sender to receiver requires intermediate stops. An agent[1] at each stop inspects the mail, and decides how to deliver it. Ultimately, an agent's job is to take the email it is given and move it one step closer to the recipient.
Mail User Agents
The first agent a user encounters is the Mail User Agent (MUA)[2] . This agent is responsible for providing email access to the user.
An MUA might provide a graphical user interface or a simple text interface to the user. Within this interface, the MUA allows users to compose, sort, save, and print their email.
Mail Delivery Agents
MUAs communicate directly with Mail Delivery Agents (MDA)[3] . MDAs are local agents, responsible for all the email within a domain. User MUAs send and receive email from their MDAs via protocols such as POP3[4] and IMAP[5].
Mail Transfer Agents
MDAs then communicate with Mail Transfer Agents (MTA)[6] . These agents move mail across the entire Internet. When an
MTA doesn't know where the recipient's domain is, it will send the email to another MTA for processing. When the MTA does know where the recipient's domain is, it will send the email directly to the domain's MDA for processing.
The image below clarifies the relationship between MUAs, MDAs, and MTAs. The arrows show how an email propagates through an MUA, into an MDA, through several MTAs, and finally back into an MDA for distribution.
The image below clarifies the relationship between MUAs, MDAs, and MTAs. The arrows show how an email propagates through an MUA, into an MDA, through several MTAs, and finally back into an MDA for distribution.
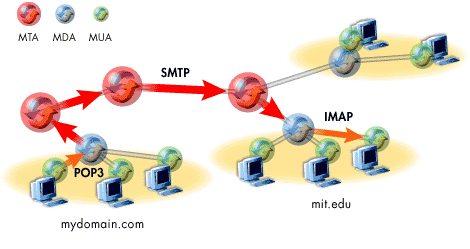
- Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs) move email between domains on the Internet Mail routing through an MTA is not intended for the MTA's domain. The MTA is only moving the email one step closer to the final recipient
- The (SMTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is the protocol responsible for moving email between MDAs and MTAs.
- Mail Delivery Agents (MDAs) receive all email bound for the domain they are in. Once receive, MDAs hold the mail until retrieved by user MUAs.
- User MUAs retrieve mail from MDAs using protocols such as POP3 and IMAP. These protocols are more powerful than SMTP, because they allow the users to manipulate their mail rather than simply transfer it.
- Mail User Agents (MUAs) allow users to read, send, print, save, and compose email. Linux supports several MUAs, from graphical to text based.
Three Email - Agents
email Agents - Exercise
Before you move to the next lesson, click the Exercise link below to practice matching email agent roles to their definitions.email Agents - Exercise
The next lesson describes the purpose of Linux MTAs and MDAs.
[1]Agent: A program in the email system that inspects an email and decides how to move it further toward the ultimate destination.
[2](MUA) Mail User Agents:Programs responsible for displaying and composing email.
[3](MDA) Mail Delivery Agents: The email agents responsible for local network email delivery.
[4]POP3: An acronym for Post Office Protocol, version 3, POP3 is an older protocol that enabled MUAs to send and receive mail from MDAs.
[5](IMAP) Internet Message Access Protocol: A standard protocol for accessing mail from your local MDA.
[6](MTA)Mail Transfer Agents: The email agents responsible for Internet-wide email delivery.